Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
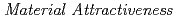 evaluation for TRU fuel cycle
evaluation for TRU fuel cycleOizumi, Akito; Sagara, Hiroshi*
Dai-43-Kai Nihon Kaku Busshitsu Kanri Gakkai Nenji Taikai Kaigi Rombunshu (Internet), 4 Pages, 2022/11
Research and development of partitioning and transmutation cycle with accelerator drive systems (ADSs) transmuting minor actinides separated from the commercial cycles has been continuously conducted to reduce the high-level radioactive waste contained in spent fuel discharged from nuclear power plants. Since the chemical form and composition of the fuels are different from those of the current commercial cycles, it is necessary to examine the inspection goal of the safeguards and the design level of physical protections which are required for the partitioning and transmutation (P&T) cycle. In previous studies, the 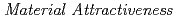 (
(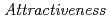 ) of the uranium (U) in the ADS fuel with a unique isotopic composition was evaluated as 2, the second highest on a 4-point scale, assuming state actors. In this study, reduction methods of potential nuclear proliferation were examined for the rationalization of the P&T cycle design considering nuclear non-proliferation. The amount of recovered U (RepU) added to the ADS fuel, which was required to increase the bare critical mass of U, was quantitatively evaluated as one of the reduction methods of potential nuclear proliferation risk. As a result, the addition of RepU, which was about 1.3- 2.7 times U in the ADS fuel, lowered the
) of the uranium (U) in the ADS fuel with a unique isotopic composition was evaluated as 2, the second highest on a 4-point scale, assuming state actors. In this study, reduction methods of potential nuclear proliferation were examined for the rationalization of the P&T cycle design considering nuclear non-proliferation. The amount of recovered U (RepU) added to the ADS fuel, which was required to increase the bare critical mass of U, was quantitatively evaluated as one of the reduction methods of potential nuclear proliferation risk. As a result, the addition of RepU, which was about 1.3- 2.7 times U in the ADS fuel, lowered the 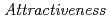 to 3 - 4. The rationalization of the P&T cycle design based on the safeguards by design can be expected by reviewing the U decontamination standards in the reprocessing steps of the commercial cycle based on these quantitative data.
to 3 - 4. The rationalization of the P&T cycle design based on the safeguards by design can be expected by reviewing the U decontamination standards in the reprocessing steps of the commercial cycle based on these quantitative data.
Tazaki, Makiko; Nakatani, Takayoshi; Shimizu, Ryo; Kimura, Takashi; Hori, Masato
Dai-43-Kai Nihon Kaku Busshitsu Kanri Gakkai Nenji Taikai Kaigi Rombunshu (Internet), 4 Pages, 2022/11
Denuclearization consists of (1) verification of nuclear activities prior to denuclearization, (2) freeze, disablement and decommissioning of nuclear weapons, nuclear materials such as HEU and Pu, their production facilities, including facilities and equipment, and their verification. In this study, as a premise for the denuclearization of nuclear materials and nuclear facilities, and with reference to the results of previous denuclearization case surveys and related literature, the denuclearization process and its options for technical measures are discussed and considered.
Nakatani, Takayoshi; Shimizu, Ryo; Tazaki, Makiko; Kimura, Takashi; Hori, Masato
Dai-43-Kai Nihon Kaku Busshitsu Kanri Gakkai Nenji Taikai Kaigi Rombunshu (Internet), 4 Pages, 2022/11
Denuclearization is the verification of nuclear development and the freezing, disabling, decommissioning, and verification of nuclear weapons, nuclear materials that can be used for nuclear weapons, and their manufacturing facilities, equipment, equipment, and materials. In this study, the technical process of measures and verification methods to effectively and efficiently achieve denuclearization at nuclear installations is examined and considered from a technical point of view.
Shimizu, Ryo; Nakatani, Takayoshi; Tazaki, Makiko; Kimura, Takashi; Hori, Masato
Dai-43-Kai Nihon Kaku Busshitsu Kanri Gakkai Nenji Taikai Kaigi Rombunshu (Internet), 3 Pages, 2022/11
no abstracts in English
Kimura, Takashi; Nakatani, Takayoshi; Shimizu, Ryo; Tazaki, Makiko; Hori, Masato
Dai-43-Kai Nihon Kaku Busshitsu Kanri Gakkai Nenji Taikai Kaigi Rombunshu (Internet), 4 Pages, 2022/11
no abstracts in English
Amano, Tsukasa; Sato, Yoshiharu; Shibata, Ryodai; Yamazaki, Katsuyuki; Shiromo, Hideo; Nakamura, Hironobu
Dai-43-Kai Nihon Kaku Busshitsu Kanri Gakkai Nenji Taikai Kaigi Rombunshu (Internet), 4 Pages, 2022/11
About ten years have passed since the introduction of nuclear security compliance and security culture development activities. While there have been changes in domestic and international situations, it is essential for nuclear security that the entire organization maintains an attitude that emphasizes compliance with laws and regulations and nuclear security. JAEA has been effectively implementing various activities with evaluation and improvement. Especially, e-learning which combines education and awareness, case studies, and internal audits are considered effective in maintaining nuclear security compliance and security culture development activities.
Fukui, Yasuhito
Dai-43-Kai Nihon Kaku Busshitsu Kanri Gakkai Nenji Taikai Kaigi Rombunshu (Internet), 3 Pages, 2022/11
After the Russian invasion on Ukrainian territory, which accompanied armed attacks in nuclear facilities in Ukraine, these incidents triggered serious concerns in Japan. Fortunately, in Japan, the necessary administrative mechanism is already established based on the currently effective laws and regulations and no additional measures are necessary to prepare for this purpose. Usually, un ordinary physical protection operations are deemed to execute in accordance with the Nuclear Reactor Regulation Act for the operators together with Japanese police and Japan coastal guards etc. However, once the unexpected incident exceeds the threshold of police-based physical protection, upon request of local governments etc., Armed Attack Situations Response Act and Civil Protection Act is activated. In addition to the ordinary physical protection, thus Prime Minister's Cabinet Office and competent authorities concerned order to protect nuclear facilities especially by Japan self-defense force, local government and designated institutions etc. in other words to protect Japanese nationals.
Lee, J.; Ito, Fumiaki*; Hironaka, Kota; Takahashi, Tone; Suzuki, Satoshi*; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Hori, Junichi*; Terada, Kazushi*
Dai-43-Kai Nihon Kaku Busshitsu Kanri Gakkai Nenji Taikai Kaigi Rombunshu (Internet), 4 Pages, 2022/11
no abstracts in English
Nagatani, Taketeru; Sagara, Hiroshi*; Kosuge, Yoshihiro*; Nakaguki, Sho; Nomi, Takayoshi; Okumura, Keisuke
Dai-43-Kai Nihon Kaku Busshitsu Kanri Gakkai Nenji Taikai Kaigi Rombunshu (Internet), 3 Pages, 2022/11
Shirafuji, Masaya; Nozaki, Teo; Akutsu, Narumi*; Miyaji, Noriko; Nakamura, Hironobu
Dai-43-Kai Nihon Kaku Busshitsu Kanri Gakkai Nenji Taikai Kaigi Rombunshu (Internet), 4 Pages, 2022/11
In order to maintain transparency in the peaceful use of nuclear materials in Japan, it is important to appropriately respond to safeguards activities conducted by the IAEA/Japan. Failure to respond appropriately to these activities could have significant impacts, such as raising suspicion from the international community about the misuse of nuclear materials by not only the operators but also by Japan. In order to strengthen activities to appropriately respond to safeguards activities, JAEA has started (I) education on safeguards for all employees directly employed by JAEA, (II) lectures, (III) case studies, and (IV) standardization of procedures related to safeguards response since FY2020, following the methods used to foster nuclear security culture in the past. This report describes these specific activities.
Omer, M.; Shizuma, Toshiyuki*; Hajima, Ryoichi*; Koizumi, Mitsuo
Dai-43-Kai Nihon Kaku Busshitsu Kanri Gakkai Nenji Taikai Kaigi Rombunshu (Internet), 3 Pages, 2022/11
Naoi, Yosuke; Noro, Naoko
no journal, ,
States are responsible for establishing, implementing and operating nuclear security regimes. There are a wide range of competent authorities and users of nuclear materials involved in the system, and it is necessary for these parties to work together to strengthen the system. Proposal of a "Nuclear Security Stakeholder Matrix" that contributes to the strengthening of the nuclear security system by identifying stakeholders for each element that constitutes the nuclear security regime, and making a matrix of their roles, responsibilities, and the knowledge and skills required to fulfill their responsibilities will be reported.